Plastic Ball: Exploring Its Uses, Benefits, and Manufacturing Process
Plastic balls are ubiquitous in our daily lives, serving various purposes across different industries. From children’s toys to industrial applications, the versatility and durability of plastic balls make them an essential component in many products and activities. This blog post will delve into the types of plastic balls, their uses, benefits, and the manufacturing process, providing a comprehensive overview of this simple yet vital object.
What is a Plastic Ball?
A plastic ball is a spherical object made from various types of plastic materials. They come in different sizes, colors, and compositions, designed to fulfill specific roles depending on their intended use. Plastic balls are preferred over other materials in many applications due to their lightweight, durability, and cost-effectiveness.
Types of Plastic Balls
1. Polyethylene (PE) Balls
Polyethylene balls are known for their high impact resistance and low density. They are often used in applications where durability and cost are critical factors.
Uses:
- Children’s toys
- Bearings and rollers
- Floatation devices
2. Polypropylene (PP) Balls
Polypropylene balls are resistant to many chemical solvents, bases, and acids. They have a high melting point and are suitable for various industrial applications.
Uses:
- Chemical storage and handling
- Laboratory equipment
- Water treatment systems
3. Nylon Balls
Nylon balls are characterized by their strength, wear resistance, and low friction. They are commonly used in mechanical and industrial applications.
Uses:
- Bearings
- Valves
- Rollers
4. Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Balls
PTFE balls, commonly known by the brand name Teflon, are highly resistant to heat, chemicals, and friction. They are used in demanding environments.
Uses:
- Chemical processing
- High-temperature applications
- Electrical insulation
5. Acetal (POM) Balls
Acetal balls, also known as polyoxymethylene balls, offer high mechanical strength, rigidity, and low friction. They are ideal for precision engineering applications.
Uses:
- Precision bearings
- Automotive parts
- Mechanical components
6. PVC Balls
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) balls are known for their excellent corrosion resistance and durability. They are often used in environments where exposure to harsh chemicals is common.
Uses:
- Water treatment
- Industrial equipment
- Outdoor toys
Benefits of Plastic Balls
1. Durability
Plastic balls are highly durable and can withstand significant wear and tear, making them suitable for both heavy-duty industrial applications and everyday use in toys and games.
2. Lightweight
Compared to metal or ceramic balls, plastic balls are much lighter. This makes them easier to handle and transport, reducing overall product weight and shipping costs.
3. Corrosion Resistance
Plastic balls are resistant to corrosion and chemical degradation, making them ideal for use in harsh environments and chemical processing industries.
4. Cost-Effective
Plastic balls are generally more affordable to produce than balls made from other materials. Their cost-effectiveness makes them a popular choice for mass production and large-scale applications.
5. Versatility
Available in various sizes, colors, and materials, plastic balls can be customized to meet specific requirements, making them versatile for a wide range of applications.
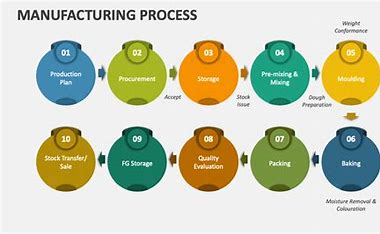
Manufacturing Process of Plastic Balls
The manufacturing process of plastic balls involves several steps to ensure they meet the desired specifications and quality standards. Here is an overview of the typical process:
1. Material Selection
The first step is selecting the appropriate plastic material based on the intended use of the balls. Factors such as strength, chemical resistance, and temperature tolerance are considered.
2. Injection Molding
Injection molding is the most common method for producing plastic balls. In this process, the chosen plastic material is melted and injected into a spherical mold under high pressure. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the balls are ejected.
3. Trimming and Finishing
After molding, the plastic balls may have excess material, known as flash, which needs to be trimmed. This step ensures that the balls have a smooth and uniform surface. Finishing processes, such as polishing or coating, may also be applied to enhance the balls’ appearance and performance.
4. Quality Control
Quality control checks are crucial to ensure that the plastic balls meet the required specifications. This involves inspecting the balls for size accuracy, surface defects, and material consistency. Any defective balls are discarded or reprocessed.
5. Packaging
The final step is packaging the plastic balls for distribution. Depending on the intended use, the balls may be packaged in bulk or individually wrapped to prevent damage during transport.
Applications of Plastic Balls
1. Toys and Recreation
Plastic balls are widely used in the toy industry, from colorful balls for ball pits to components in various games and sports equipment. Their lightweight and durable nature make them safe and enjoyable for children.
2. Industrial Applications
In industrial settings, plastic balls serve as components in machinery and equipment. They are used in bearings, rollers, and valves due to their low friction and wear resistance.
3. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
Plastic balls are utilized in the chemical and pharmaceutical industries for their resistance to corrosion and chemical degradation. They are used in storage tanks, mixing equipment, and filtration systems.
4. Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive and aerospace industries, plastic balls are used in applications requiring lightweight and durable materials. They are found in fuel systems, electrical components, and various mechanical parts.
5. Water Treatment
Plastic balls play a crucial role in water treatment systems. They are used in filtration, aeration, and flotation devices to improve water quality and efficiency.
6. Medical Devices
In the medical field, plastic balls are used in various devices and equipment. Their biocompatibility and resistance to sterilization processes make them suitable for applications such as medical implants, diagnostic tools, and surgical instruments.
Conclusion
Plastic balls are versatile and essential components in a wide range of applications, from children’s toys to industrial machinery. Their durability, lightweight nature, and cost-effectiveness make them an attractive choice for many uses. Understanding the different types of plastic balls, their benefits, and the manufacturing process can help in selecting the right ball for specific needs. Whether for play, industry, or medical use, plastic balls continue to play a significant role in modern technology and everyday life.

